Verschieben von CA-Zertifikaten in den Systemspeicher auf gerooteten Geräten
Dieser Artikel behandelt AdGuard für Android, einem multifunktionalen Werbeblocker, der Ihr Gerät auf Systemebene schützt. Um zu sehen, wie es funktioniert, laden Sie die AdGuard-App herunter
AdGuard für Android kann verschlüsselten HTTPS-Verkehr filtern und damit die meisten Anzeigen und Tracker auf Websites sperren. Auf gerooteten Geräten können Sie mit AdGuard auch den HTTPS-Datenverkehr in Apps filtern. Für die HTTPS-Filterung muss das CA-Zertifikat von AdGuard in die Liste der vertrauenswürdigen Zertifikate aufgenommen werden.
Auf nicht gerooteten Geräten können CA-Zertifikate in den Benutzerspeicher installiert werden. Nur eine begrenzte Anzahl von Apps (vor allem Browser) vertrauen CA-Zertifikaten, die im Benutzerspeicher installiert sind, was bedeutet, dass die HTTPS-Filterung nur bei diesen Apps funktioniert.
Auf gerooteten Geräten können Sie ein Zertifikat im Systemspeicher installieren. Dadurch kann AdGuard den HTTPS-Datenverkehr auch in anderen Apps filtern.
Und so geht's.
So installieren Sie das Zertifikat von AdGuard im Systemspeicher
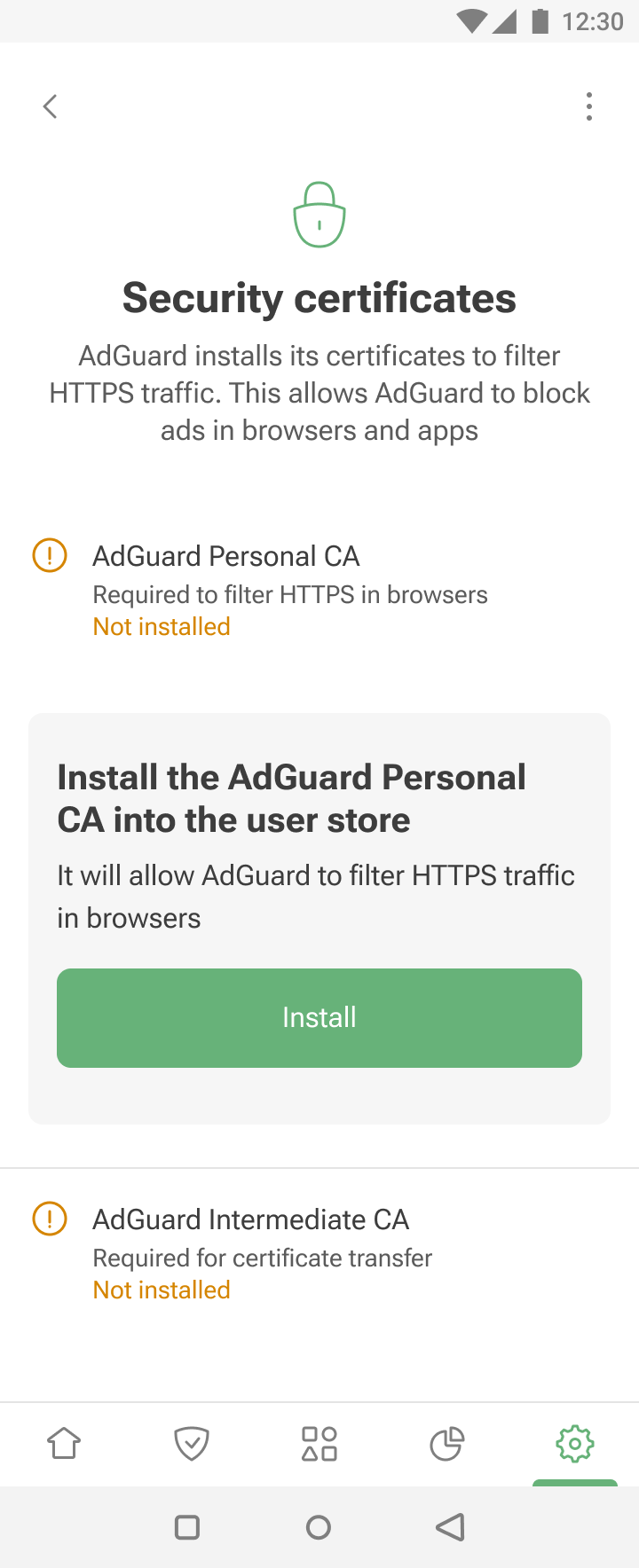
Öffnen Sie AdGuard → Einstellungen → Filterung → Netzwerk → HTTPS-Filterung → Sicherheitszertifikate.
Wenn Sie noch kein Zertifikat haben, installieren Sie das AdGuard Personal CA in den Benutzerspeicher. Dies ermöglicht es AdGuard, HTTPS-Verkehr in Browsern zu filtern.
Installieren Sie das AdGuard Intermediate CA in den Benutzerspeicher. Sie benötigen es, um das Magisk-Modul adguardcert auszuführen, mit dem Sie Zertifikate in den Systemspeicher verschieben können.
Installieren Sie die neueste Version des Magisk-Moduls adguardcert.
Öffnen Sie Magisk → Module → Aus Speicher installieren und wählen Sie die heruntergeladene adguardcert-Datei aus. Das AdGuard Personal CA-Zertifikat wird in den Systemspeicher kopiert.
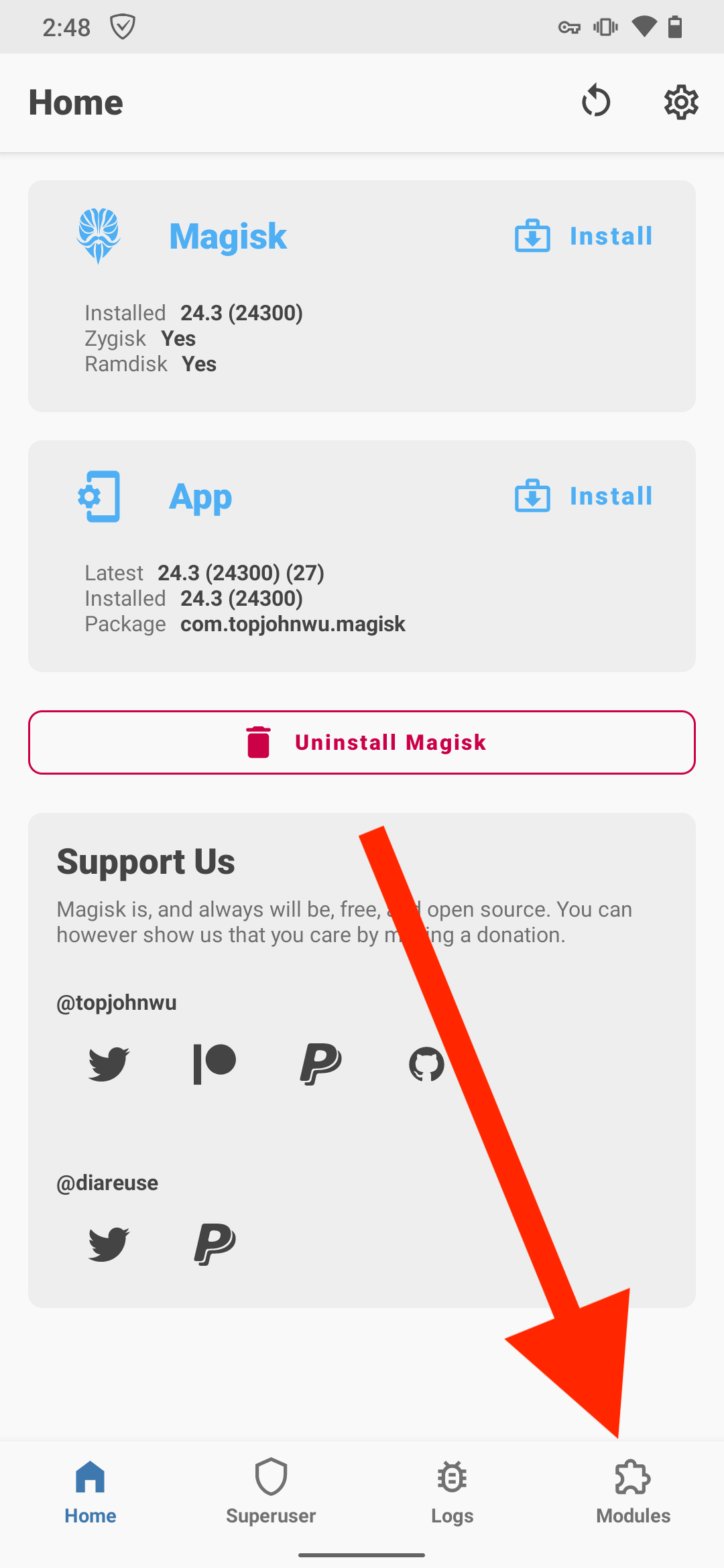


Tippen Sie auf Neu starten.

Nach der Übertragung ermöglicht das AdGuard Personal CA im Systemspeicher die Filterung des HTTPS-Verkehrs in Apps, während das AdGuard Intermediate CA im Benutzerspeicher die Filterung des HTTPS-Verkehrs in Chromium-basierten Browsern ermöglicht (siehe unten warum).
Bekannte Probleme mit Chrome und Chromium-basierten Browsern
Chrome und andere Chromium-basierte Browser erfordern Certificate Transparency (CT)-Protokolle für Zertifikate, die sich im Systemspeicher befinden. Die CT-Protokolle enthalten keine Informationen über Zertifikate, die von Apps zur HTTPS-Filterung ausgestellt wurden. Daher benötigt AdGuard ein zusätzliches Zertifikat im Benutzerspeicher, um den HTTPS-Verkehr in diesen Browsern zu filtern.
Bromite-Browser
Zusätzlich zu dem oben genannten Problem vertraut Bromite den Zertifikaten im Benutzerspeicher standardmäßig nicht. Um dort den HTTPS-Verkehr zu filtern, öffnen Sie Bromite, gehen Sie zu chrome://flags und setzen Sie Benutzerzertifikate zulassen auf Aktiviert. Dies gilt sowohl für gerootete als auch für nicht gerootete Geräte.