How to automate AdGuard for Android
Cet article concerne AdGuard pour Android, un bloqueur de publicité multifonctionnel qui protège votre appareil au niveau système. Pour voir comment ça fonctionne, téléchargez l'application AdGuard
Many people choose Android because they like customizing settings and want to control their device completely. And it's totally normal if some of AdGuard users are not satisfied with its default behavior. Let's say, you want protection to stop when a certain app is launched, and then restart it again when the app is closed. This is a job for the Tasker app.
AdGuard interface
There are a lot of tasker apps out there, for example Tasker, AutomateIt etc. AdGuard provides an interface that allows these apps to setup various automation rules.
Thanks to this interface, any app can send a special message (called “intent”) that contains the name of the action and some additional data, if needed. AdGuard will look at this intent and perform the required actions.
Security concerns
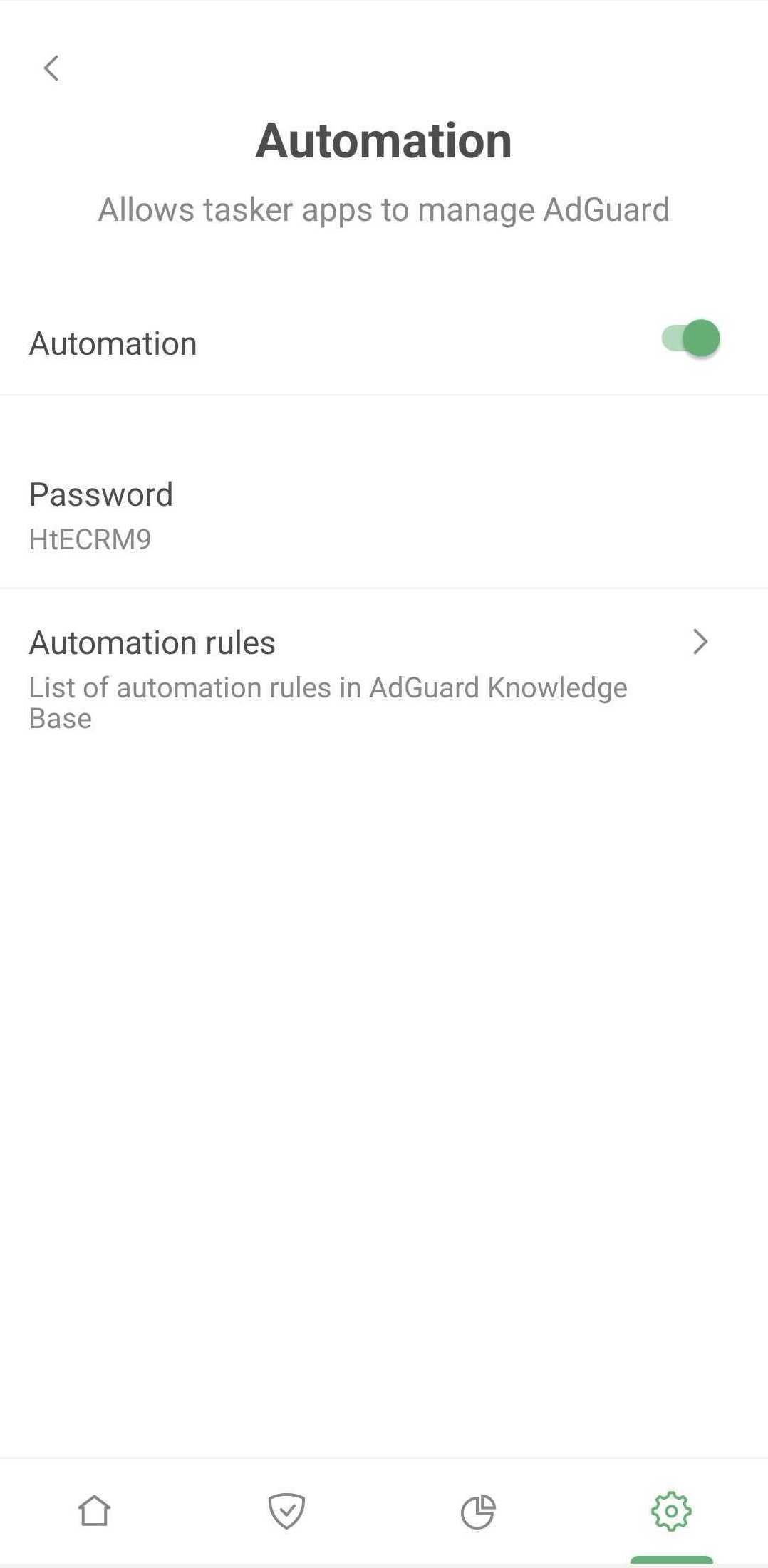
Isn't it dangerous to let some random apps manage what AdGuard does? It is, and that's why a password is sent along with the intent. This password will be generated by AdGuard automatically, but you can, of course, change it at any time.
Available actions
Here are actions that, when included in the intent, will be understood by AdGuard:
start starts the protection, no extra data is needed;
stop stops the protection, no extra data required;
pause pauses the protection. The difference between this and stop is that a notification will appear that restarts the protection when you tap it. No extra data required;
update checks for available filter and app updates, no additional data is needed;
dns_filtering turns DNS filtering on and off. Requires an extra flag:
enable:true or enable:false enables or disables DNS filtering, accordingly.
fake_dns allows resolving DNS requests on the specified proxy server. This requires an extra flag:
enable:true or enable:false enables or disables the Use FakeDNS setting, respectively.
::note
Lorsque le paramètre Utiliser FakeDNS est activé, la Protection DNS sera automatiquement désactivée. DNS requests won't be filtered locally.
:::
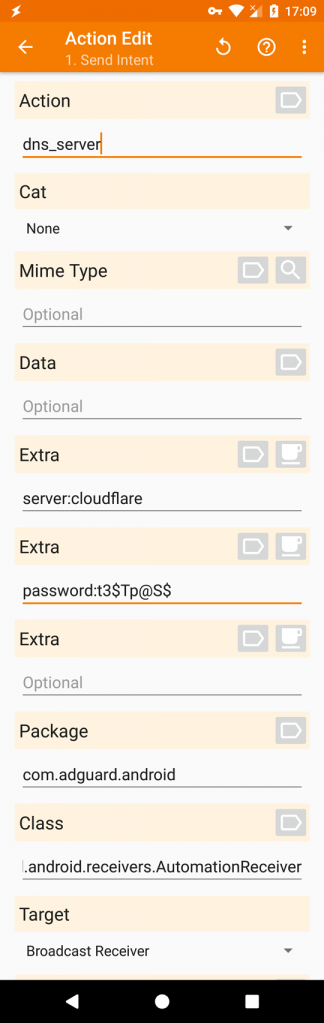
dns_server switches between DNS servers, you need to include additional data:
server:adguard dns switches to AdGuard DNS server;
::note
The full list of supported provider names can be found in our known DNS providers list.
:::
server:custom switches to the previously added server named custom;
server:tls://dns.adguard.com creates a new server and switches to it if the previously added servers and providers don't contain a server with the same address. Otherwise, it switches to the respective server. You can add server addresses as IP ( regular DNS), sdns://… (DNSCrypt or DNS-over-HTTPS), https://… (DNS-over-HTTPS) or tls://... (DNS-over-TLS);
server:1.1.1.1, tls://1.1.1.1 creates a server with comma separated addresses and switches to it. When adding a server via server:1.1.1.1, tls://1.1.1.1, the previously added server is removed.
server:system resets DNS settings to default system DNS servers.
proxy_state enables/disables the outbound proxy. Requires an extra flag:
enable:true or enable:false activates or deactivates the outbound proxy, accordingly.
proxy_default sets the proxy from the list of previously added ones as default or creates a new one if server has not been added before.
You need to specify additional data:
server:[name] where [name] is the name of the outbound proxy from the list.
Or you can configure server parameters manually:
server:[type=…&host=…&port=…&username=…&password=…&udp=…&trust=…].
proxy_remove removes the proxy server from the list of previously added ones.
server:[name] where [name] is the name of the outbound proxy from the list.
Or you can configure remove parameters manually:
server:[type=…&host=…&port=…&username=…&password=…&udp=…&trust=…].
- Compulsory parameters:
[type] — proxy server type:
- HTTP
- SOCKS4
- SOCKS5
- HTTPS_CONNECT
[host] — outbound proxy domain or IP address;
[port] — outbound proxy port (integer number from 1 to 65535);
Optional parameters:
[login and password]— only if proxy requires it. This data is ignored when setting up SOCKS4;[udp]applied only on SOCKS5 server type and include option UDP through SOCKS5. It is necessary to set true or false value;[trust]applies for HTTPS_CONNECT server type only and include option Trust any certificates. It is necessary to set true or false value.
setting by name: server:MyServer
manually settings: server:host=1.2.3.4&port=80&type=SOCKS5&username=foo&password=bar&udp=true
Don't forget to include the password, package name, and class. You need to do so for every intent.
Extra: password:*******
Package name: com.adguard.android
Class: com.adguard.android.receiver.AutomationReceiver
::note
Before v4.0 the class was called com.adguard.android.receivers.AutomationReceiver but then we changed its name to com.adguard.android.receiver.AutomationReceiver. If this function is used, remember to update to the new name.
:::
Exécution sans notification
Pour effectuer une tâche sans afficher de toast, ajoutez un EXTRA supplémentaire quiet: true
Exemple