AdGuard’s digest: Bard lands in EU, Google goes all in on data-scraping, tax sites abuse privacy, EU and US have a deal
In this edition of the AdGuard digest: Google’s AI chatbot comes to the EU after a privacy hiccup, Shutterstock satisfies OpenAI’s appetite for data, tax filing sites leak personal data, the EU and US take another shot at a data transfer deal, as Google’s replacement for tracking cookies comes under scrutiny in France.
Google’s Bard AI chatbot launches in EU after privacy delay
Google’s answer to OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Microsoft’s Bing AI has finally launched in Europe, expanding its geographic reach to over 230 countries. It comes after Bard was derailed last month on its way to EU release by the Irish data protection watchdog. Back in June, the Irish regulator said that Google had failed to provide enough information to show that it was compliant with European data privacy laws.
Since then Google has updated Bard’s interface to include a link to Google’s “privacy hub” that explains in detail how users can limit Bard’s access to their data. Users have the option to turn off Bard’s activity, which means it will no longer be stored in their Google account, as well as delete their past chats. However, Google notes that even with Bard Activity turned off, it will still retain chats for 72 hours “to provide the service” and “to process feedback.” A privacy notice displayed by Bard urges
users “not to include information that can be used to identify you or others,” since it can be reviewed by humans — underpaid and overworked third-party contractors, presumably.
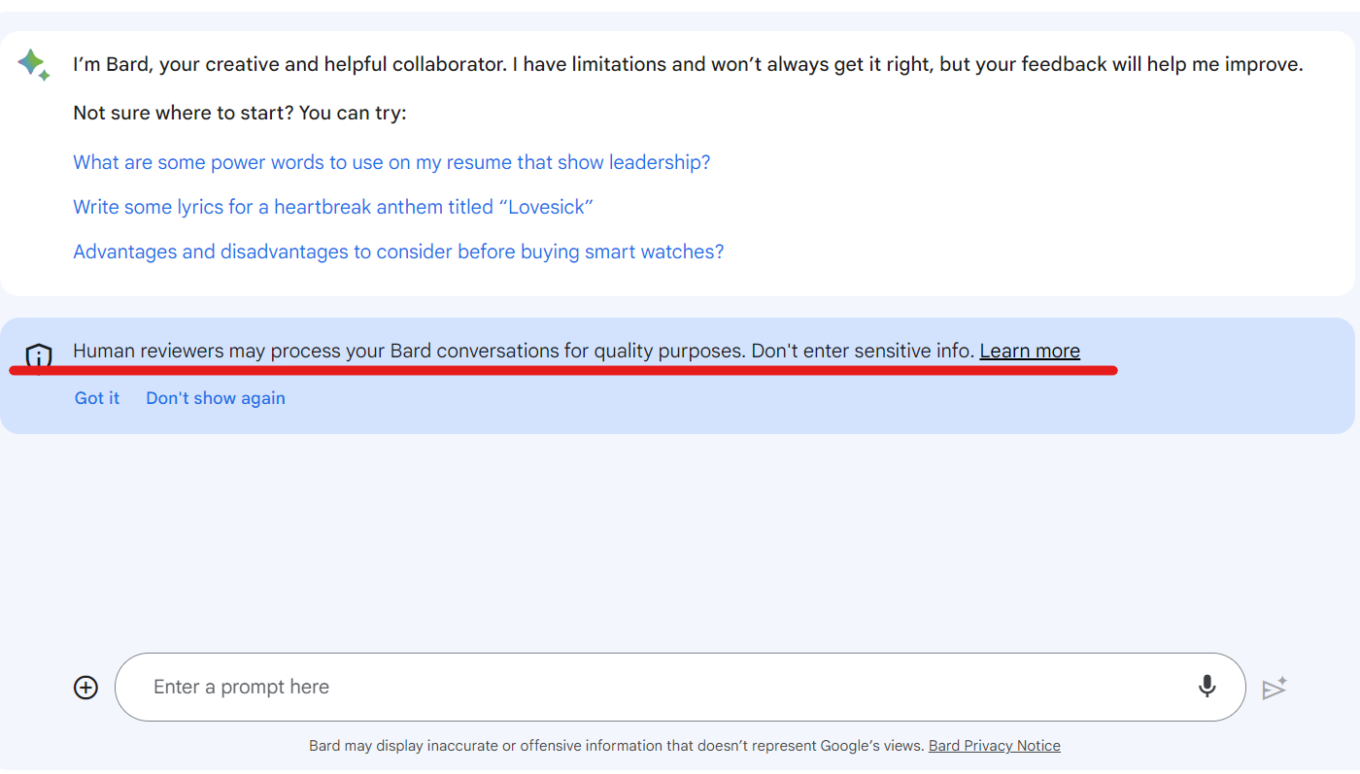
The fact that Google has been forced to make the information about Bard’s data processing readily available to users and offer them more privacy options is a good thing. However, Bard’s privacy policy still remains vague and seems to leave loopholes for Google to continue harvesting data. So, heeding Google’s advice (yes, you heard this right) will be the best option this time: do not entrust Bard with any of your sensitive data.
Tax prep sites leak sensitive user data to Meta and Google
An investigation by US lawmakers has revealed that tax preparation websites have been handing over sensitive personal and financial data to Meta and Google for years, in possible violation of privacy laws. The culprits are TaxAct, H&R Bloсk, and TaxSlayer, who placed Meta and Google’s tracking codes on their websites, giving the big tech giants access to the confidential information of millions of taxpayers.
The report zooms in on Meta’s tracking practices, which were first exposed by The Markup last year. The websites shared all kinds of data with Meta, such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, and gender as hashes, as well as filing status, refund amount, taxes owed, and dependents’ names. Meta even got data on whether users qualified for deductions or exemptions. Meta then used this information to target ads to taxpayers across the web, and to train its AI algorithms. Lawmakers slammed both Meta and Google for their “stunning disregard for taxpayer privacy.” The report also notes that while both companies claimed to have filtering systems in place to prevent the collection of sensitive taxpayer data, those systems were apparently “ineffective.”
The investigation confirmed that Meta and Google exploited tax preparation sites to get their hands on sensitive taxpayer information without their explicit consent or knowledge, which once again shows that their priorities are in data harvesting, not data protection. It’s good to see that US lawmakers are trying to hold big tech companies accountable, and not just the tax prep sites (who claim they didn’t know they were sending the sensitive taxpayer data). Users deserve to have their privacy and data protected, especially their personal and financial information.
Shutterstock allows OpenAI to train AI on its images for 6 more years
The world’s largest stock image site, Shutterstock, will continue allowing OpenAI, the company behind ChatGPT and DALLE-E, to use its vast library of images, videos, music, and associated metadata to train AI. OpenAI and Shutterstock first partnered in 2021, and the partnership has now been expanded and extended for an additional 6 years. Shutterstock’s partnership with OpenAI previously saw the stock photo site directly integrate an DALLE-E image generator into its platform.
Shutterstock promised to compensate those artists whose works would be used for training its generative AI, as well as pay royalties for “newly generated assets.” Last year, Shutterstock became the first in the industry to launch a contributor fund in an attempt to make things right with creators, irate over the fact that their images were being scraped to make AI art. Shutterstock’s approach to AI is drastically different from that of Getty Images, which banned AI-generated images outright over fears of future copyright infringement claims.
AI companies and artists have long been at odds over the use of their work for AI training and generation. The legal and ethical issues are complex and unresolved. Shutterstock is trying to balance both sides by compensating artists and giving them an option to opt out, but it’s hard to say if that’s enough or even enforceable. We will have to wait and see which approach, embracing or rejecting AI art, prevails. In the meantime, OpenAI faces increasing pressure from regulators, including from the US goverment which investigates it for potentially harming consumers through data collection and “hallucinations.”
Google’s replacement for tracking cookies requires consent, says watchdog
We have written and railed extensively about Google’s replacement for third-party cookies in Chrome called “Topics.” Topics are part of Google’s Privacy Sandbox initiative to make targeting for personalized ads more privacy-friendly. Despite widespread criticism that it fails to do so, including from Apple, Mozzila, and AdGuard, Google has moved forward with the implementation of Topics. Since July, Google has been allowing sites to test its features as part of a transition period before it completely deprecates third-party cookies in the second half of 2024.
Now, the French privacy watchdog, CNIL, has clarified the legal obligations of developers who want to test Google’s new tracking method. The watchdog said that, as with cookies before, developers would have to ask users’ permission to track them with the new method.
The French privacy watchdog’s decision is significant because it implies that the new and supposedly privacy-friendly tracking method, Topics, is not foolproof and may not be that drastically different from the old tracking cookie. It also seems to validate our concerns that Topics will not prevent tracking of users by larger platforms, such as Google itself. AdGuard users don’t need to worry though: we’ve already committed to blocking the Topics API.
Google hit with lawsuit after saying it will scrape all Internet to train AI
Google’s attempt to claim that it has every right to scrape everything you post online to train its AI models has backfired, with its now facing a class-action lawsuit for “harvesting data in secret” to create AI products. Google recently updated its privacy policy to state that it “uses publicly available information to help train Google's AI models and build products and features like Google Translate, Bard, and Cloud AI capabilities.”

Historic differences between Google’s old and updated privacy policies. The current version is in green. Source: Google
Such audacity drew a backlash from privacy activists, and now Google is facing a lawsuit seeking billions in punitive damages. The plaintiffs argue that Google’s activities amount to stealing in plain sight, and that it could have obtained the data legally instead. “Google had options other than to steal personal and copyrighted information. Internet data is available for purchase just like any other content or property,” the lawsuit says.
It’s encouraging to see that Google’s ongoing data grab is being challenged and exposed, and that more people are becoming aware of what’s going on behind the scenes. Hopefully, this will deter Google from using online data as its own without compensation or the ability to opt out. Although, we may be hoping for too much.
US and EU agree on deal to transfer personal data across Atlantic
The EU has approved a deal aimed at making the transfer of personal user data between the US and the EU legal again. The deal comes about three years after EU court quashed the previous pact, called “Privacy Shield,” which resulted in a legal void and multimillion-dollar fines for companies that continued to send European data to the US.
But it’s too early to celebrate the deal. Privacy advocates argue that it is not that different from previous proposals that were deemed inadequate by EU bodies. NOYB, a privacy group that has successfully challenged previous deals, called the new agreement “largely a copy of the failed Privacy Shield” and said it would also challenge it in court.
We’ll be following the situation closely, and in the meantime, stock up on popcorn.