Popular Chrome extensions, including ad blockers, got hijacked. Learn how to protect yourself
In February 2025, GitLab Threat Intelligence team identified at least 16 malicious Chrome extensions affecting over 3.2 million users. These extensions used to be legit, installed through official browser stores from the trusted developers, but were later corrupted via malicious ‘updates’.
The investigation has determined that this attack originated from compromised developer accounts. Some developers stopped supporting their extensions beforehand, thus losing control over them, while others, still in charge, were likely deceived through the phishing kits.
Malicious extension updates introduced hidden scripts that covertly stole data, modified web requests, and injected ads into websites. These changes largely went unnoticed by users, as they had already granted the necessary permissions, allowing attackers to manipulate web content and user interactions seamlessly.
What risks do users face?
It is unclear what damage was caused by this particular malicious campaign, but permissions such as ‘host access’ and ‘scripting controls’ pose significant risks, as they enable the extraction of sensitive information, including credit card details, login credentials, authentication tokens, and cookies — potentially granting attackers control over user accounts or access to private messages.
Extensions can also modify webpage content in real time, creating opportunities for fraud, such as altering transaction details on banking websites to mislead users. Additionally, attackers can inject advertisements, redirect users to phishing sites, or generate fake clicks to exploit ad revenue.
The users of the affected extensions left multiple comments in the Chrome Web Store, suggesting that the extensions had gone rogue at some point. Among other things, the users noticed strangely placed ads, affiliate IDs added to service links, and issues with console.log — a built-in function used for debugging and code analysis:
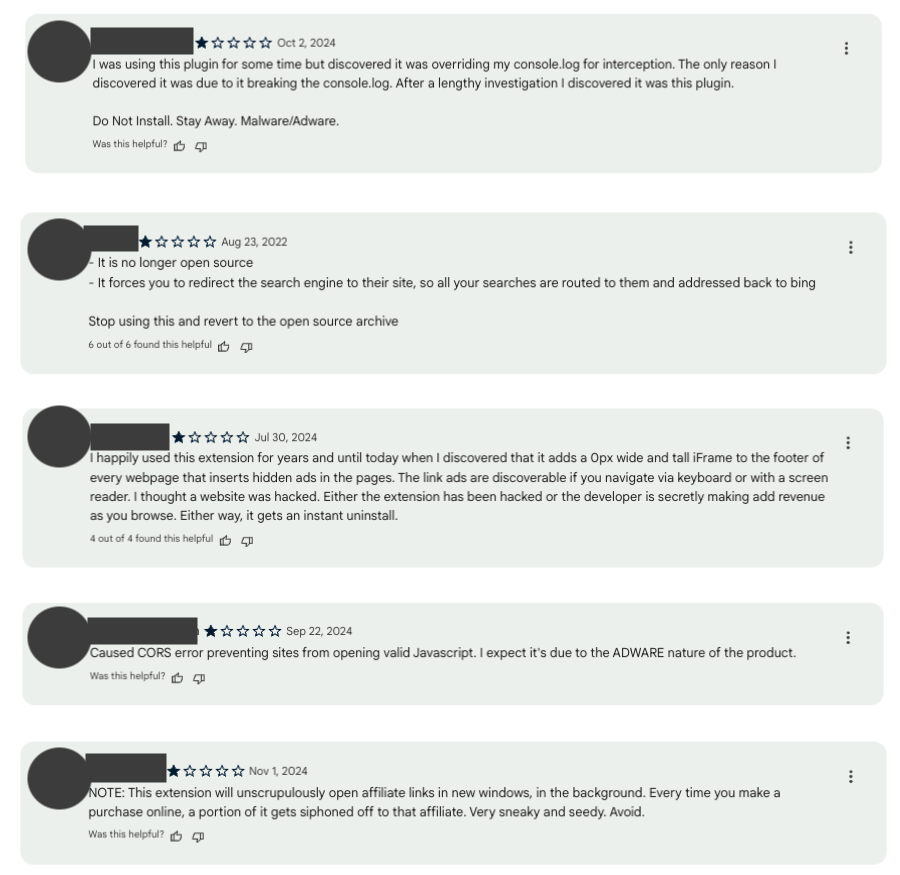
Source: GitLab Security Tech Notes
Ad blockers and the matter of trust
A total of 16 extensions were compromised, their full list available on the research page. What stood out to us, however, was that three of these were ad blockers (Adblocker for Chrome — NoAds, Adblock for You, and Adblock for Chrome).
As an ad blocker ourselves, we find this particularly concerning. Five years ago, we exposed 'fake' ad blocking extensions engaged in cookie stuffing for ad fraud. These extensions, controlled remotely, silently injected affiliate cookies into users' browsers. Critically, some of those extensions were so-called 'time bombs,' poised for more malicious actions once given a further command from a remote server. So, bottom line: choosing a trustworthy ad-blocking solution is paramount; the consequences of a poor choice can be severe.
In this case, the extension developers had no malicious intent. Their extensions were originally safe but later compromised by threat actors. However, as a general precaution, we once again recommend following these guidelines:
- Only install extensions from reputable sources, such as official stores or verified websites
- Research the developer before installing
- Review the privacy policy to understand data usage
- Be cautious when granting permissions, especially if an extension requests excessive access
- Regularly remove extensions you no longer use to minimize the risk of malicious updates
Users often grant permissions without fully understanding their implications, especially if an extension appears useful or reputable. Once granted, these permissions remain in effect until the extension is removed, allowing attackers to exploit them over time. And as we can see, since extensions update automatically, a trusted extension can later introduce malicious updates, compromising user security without notice.
Now, the affected extensions have already been removed from the Chrome store, but users should also remove them from their devices and stay vigilant to protect themselves from similar incidents in the future.
Check this issue of our TechTok series to learn more about how to determine which apps and extensions are to be trusted. Stay alert and prioritize security in your choices!